
A VA loan is a mortgage program established by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) to help servicemembers, veterans, and eligible surviving spouses purchase, build, or refinance homes. The VA does not directly lend money but guarantees a portion of the loan, enabling private lenders to offer favorable terms.

Key Features
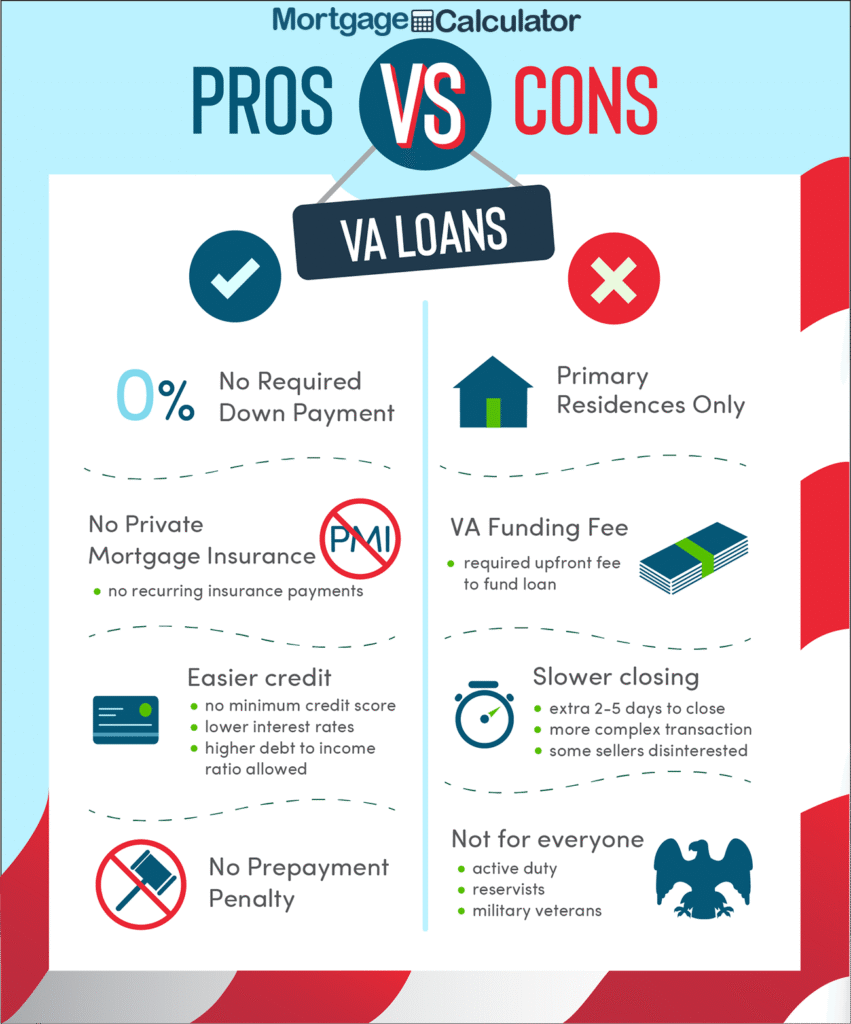
- No Down Payment: Most VA loans require no down payment, making homeownership more accessible for veterans and servicemembers.
- No Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI): Borrowers are not required to pay PMI, which can save hundreds per month compared to conventional loans.

- Competitive Interest Rates: VA loans typically offer lower interest rates-often 0.5% to 1% lower than conventional loans-resulting in significant savings over the life of the loan.
- Limited Closing Costs: The VA limits the closing costs lenders can charge, and some costs can be paid by the seller.
- No Prepayment Penalty: Borrowers can pay off their VA loan early without penalty.
- Flexible Credit Requirements: While the VA does not set a minimum credit score, most lenders have their own benchmarks, which are generally more lenient than those for conventional loans.

Eligibility
To qualify for a VA loan, applicants must meet at least one of the following criteria:
- Active-duty servicemembers with a minimum period of service.
- Veterans who meet length-of-service requirements.
- Certain surviving spouses of veterans.
- Members of the National Guard and Reserves may also qualify.
A Certificate of Eligibility (COE) from the VA is required to prove eligibility. This can be obtained through the VA website or with the help of a lender4.
Types of VA Loans
| Loan Type | Description |
|---|---|
| VA Purchase Loan | Used to buy a primary residence with no down payment and no PMI. |
| VA Cash-Out Refinance | Allows borrowers to convert home equity into cash or refinance a non-VA loan. |
| VA Interest Rate Reduction Refinance Loan (IRRRL) | Streamlines refinancing to a lower rate or better terms for existing VA loans. |
| VA Renovation Loan | Finances both the purchase/refinancing and repairs/upgrades in a single loan. |
| VA Energy Efficient Mortgage (EEM) | Finances energy-efficient home improvements. |
| Native American Direct Loan | For eligible Native American veterans to buy/build/improve homes on federal trust land. |
VA Loan Funding Fee

Most VA loans require a one-time funding fee, ranging from about 1.4% to 3.6% of the loan amount, depending on factors like down payment size and whether it’s a first-time or subsequent use. Some veterans, such as those receiving VA disability compensation, are exempt from this fee.

Advantages
- Affordability: No down payment and lower interest rates make homeownership more affordable.
- Flexible Use: VA loans can be used for various purposes-buying, building, refinancing, or upgrading homes.
- Assumability: VA loans can be assumed by qualified buyers, allowing them to take over the existing mortgage and its interest rate, which can be a major advantage in a rising rate environment.

Potential Drawbacks
- Funding Fee: The mandatory funding fee increases costs, though it is often rolled into the loan.
- Primary Residence Only: VA loans are intended for primary residences, not investment properties or vacation homes.
- Lender Participation: Not all lenders offer VA loans, so options may be limited in some areas.

How VA Loans Work
The VA guarantees a portion of the loan, reducing the risk for lenders. This guarantee allows lenders to offer better terms, such as no down payment and no PMI. The process involves:
- Obtaining a Certificate of Eligibility.
- Applying through a participating private lender.
- Meeting both VA and lender-specific requirements.
- Closing on the loan, with the VA guaranteeing a portion of the mortgage.

Special Programs and Protections
- Assistance for Borrowers in Trouble: The VA can provide financial counseling and assistance to help borrowers avoid foreclosure.
- Adapted Housing Grants: For veterans with service-connected disabilities, the VA offers grants to buy, build, or modify homes for better accessibility.
- Flexible Income Considerations: Military allowances and special pays can be counted as income for qualifying.
Recent Updates
- Loan Limits: As of recent legislative changes, veterans with full entitlement no longer face county-level loan limits. They can borrow as much as they qualify for without a down payment. Limits still apply for those with partial entitlement.
- Credit Score Flexibility: While the VA does not set a minimum credit score, most lenders require a score of at least 620, but exceptions are possible.

Conclusion
The VA loan program is a powerful benefit for eligible veterans, servicemembers, and their families, offering unique advantages like no down payment, no PMI, and competitive rates. These features make homeownership more accessible and affordable, with special protections in place for those who serve. However, borrowers should consider the funding fee and ensure their lender participates in the program before proceeding.